


Despite the immense size of even the smallest galaxies, most galaxies in the heavens are not visible to the naked eye. As optical-light (visible to humans) telescopes became more and more powerful, more and more galaxies and stars became visible. In the present era, high-definition images are created at electromagnetic wavelengths that are far shorter and far longer than the wavelength band of human vision; thus, opening our field of view to an extraordinarily wide window of observation. Explore electromagnetic wavelengths at "What Our Eyes Cannot See"

As time marches on, formation of colonies on the Moon and Mars will be routine events. On a negative note, however, visiting other solar systems in our own galaxy represents a major challenge, the constricting factor being the maximum speed of light:
Note:
The symbol" ~ " (tilde) , as used by this author, is shorthand for "approximately " or "about ." The tilda has other meanings in languages other than English.
Our nearest neighboring star (
Just a Speculation: Our future journeys into outer space will necessarily be via self-contained, closed-loop habitat vehicles that self-produce food, textiles, building materials, and electricity. Solar energy would not be available for most of a trip, because of the great distances between the spaceship and nearby stars; brightness diminishes by the distance squared (; i.e. brightness is inversely proportional to the distance squared.Because of the immense distance traveled from Earth, a journey of this nature must also include plans for the next generation that must proceed from the first generation of travelers. A one-way trip to our nearest star would require the implementation of, for example, social and legal structures and rules for civility and procreation. In other words, new civilizations would evolve.
The foregoing issues might seem insurmountable. If the history of the past 100 years or so is an example of what can be revolutionary application of old and new technologies, we should have faith that new technologies and human ingenuity will arise as needed. The most needed new technology is the unlimited production of energy. Although, we can see the future of energy production by gazing into the sky, the Sun and stars have continued to leave us with many gaps in our understanding of their energy-producing miracle; perhaps we can baptise this miracle, "
energy of the gods ".

Before the late 19th century, the heavens were viewed only in

Another example of advancements in inaging is seen in the
photographs of Andromeda (M31) taken in 1898 by Isaac Roberts that began to establish M31 as a galaxy,
NASA's space-based Hubble telescope revealed an immense amount of image detail shown in this zoomed-in view of one tiny area of the original Andromeda image. Extreme (4k imagery) magnification uncovers innumerable stars.


At a distance from Earth of
To carry this idea of relative distance a bit further, our Sun is only
One may have wondered why there is a noticeable gap of silence when two people are talking to each other via satellite. The speed of light explains the phenomenon. Because all electromagnetic radiation travels at or near the speed of light, a
Note:Light travels down a fiber-optic cable (very thin sttrands of glass) near the maximum speed of light;electrons travel down a copper wire also at, or nearly at, the speed of light.
Communicating here on Earth, however, does not have a noticeable delay, because the maximum distance between any two points anywhere on the surface of the Earth is about

Many of the stars that appear to us on Earth at this time in history will no longer be alive in the future and, conversely, many new stars will have replaced old stars that are in our view now. Millions of years from now, the sky will be different; our own Milky Way galaxy will be different. Ancient Asian and Latin philosophers observed that "
To put these ideas into some semblance of comprehension, realize that our Earth is 4.5 billion years old. About 4-billion years from now, the Andromeda Galaxy and our Milky Way galaxy will have begun the process of colliding with each other, dramatically changing the geography of this part of the Universe. Galactic collisions are a common occurrence in our Universe.
Will our Universe die?, at the end of "Creation", or will our Universe not die? Is our Universe forever, perhaps? How might new discoveries and the magic of "quantum physics" shape space, time, and reality? No one knows, yet!
Return to top of this page

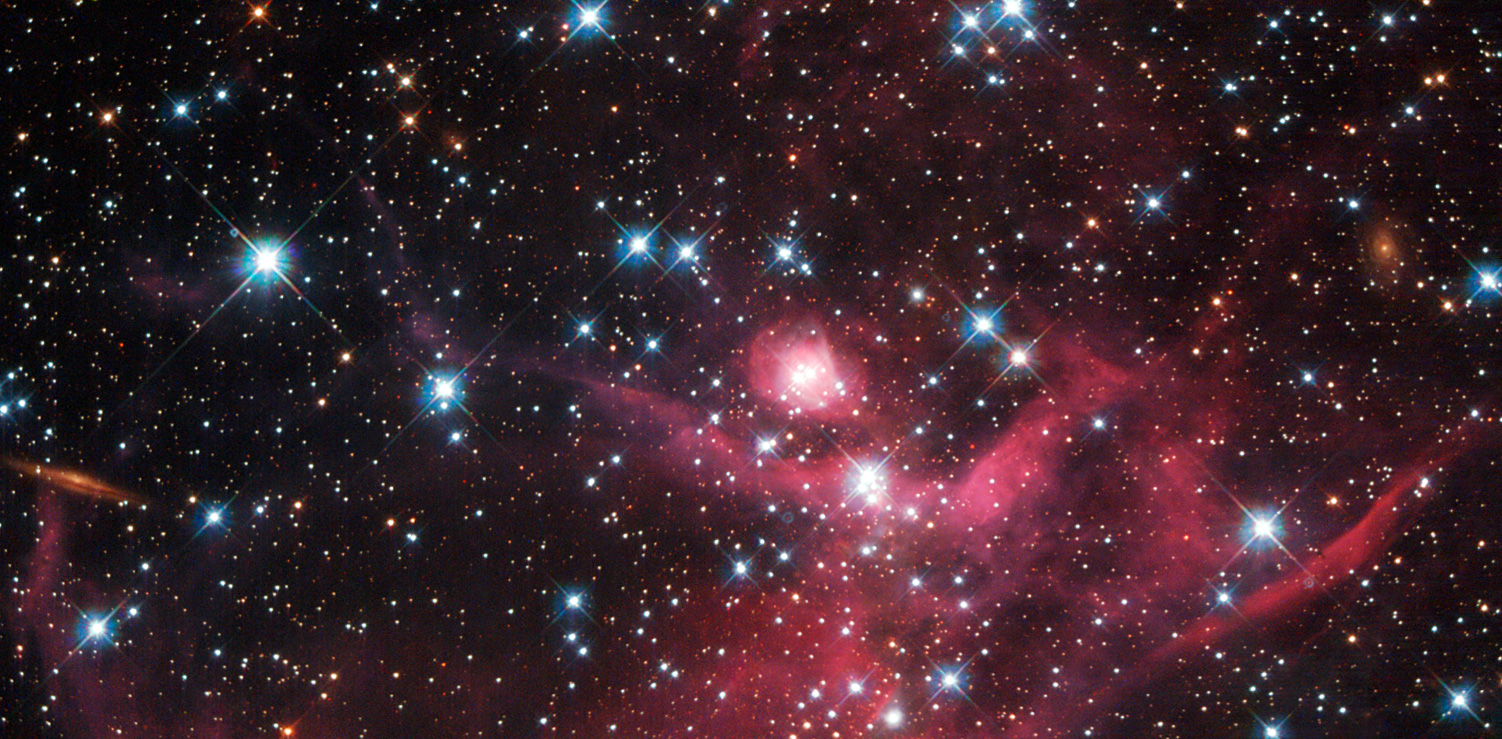
- ☀ Dwarf Galaxies Contains
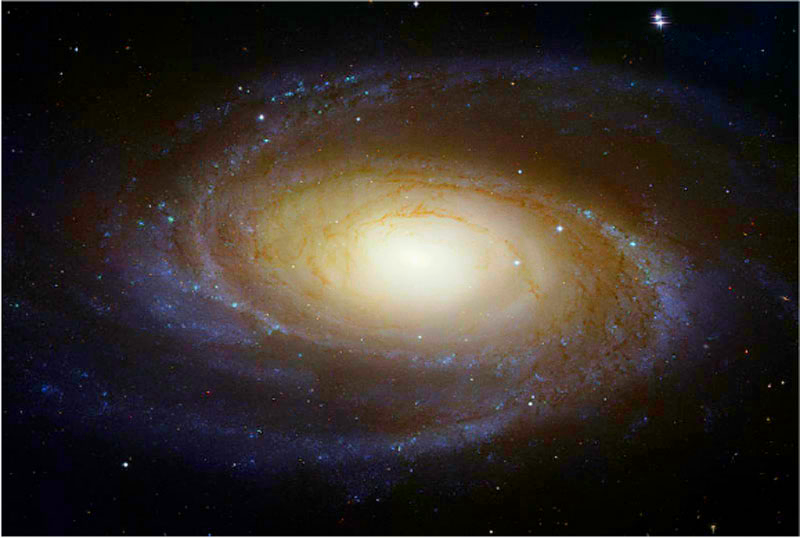
youngest stars- ☀ SpiralMilky Way Galaxy
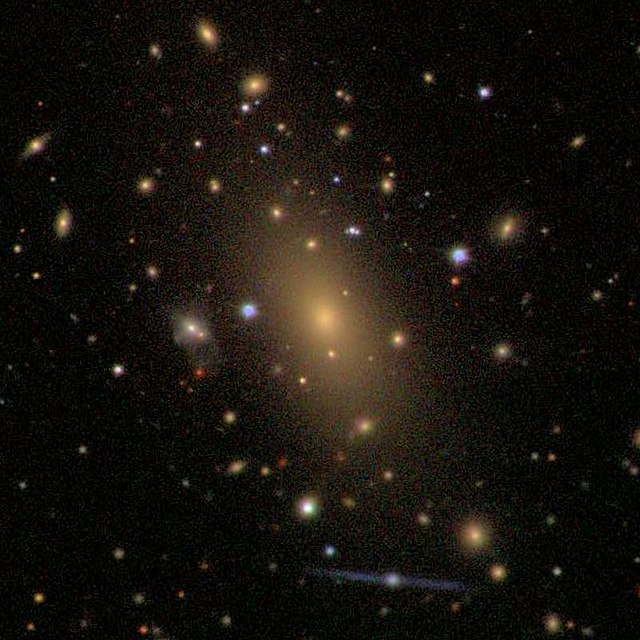
- ☀ EllipticalSombrero Galaxy
- ☀ Globular ClustersMessier 2
- ☀ IrregulerMagellanic Clouds
- ☀ Super GiantContains
oldest stars

Galaxies are classified by their


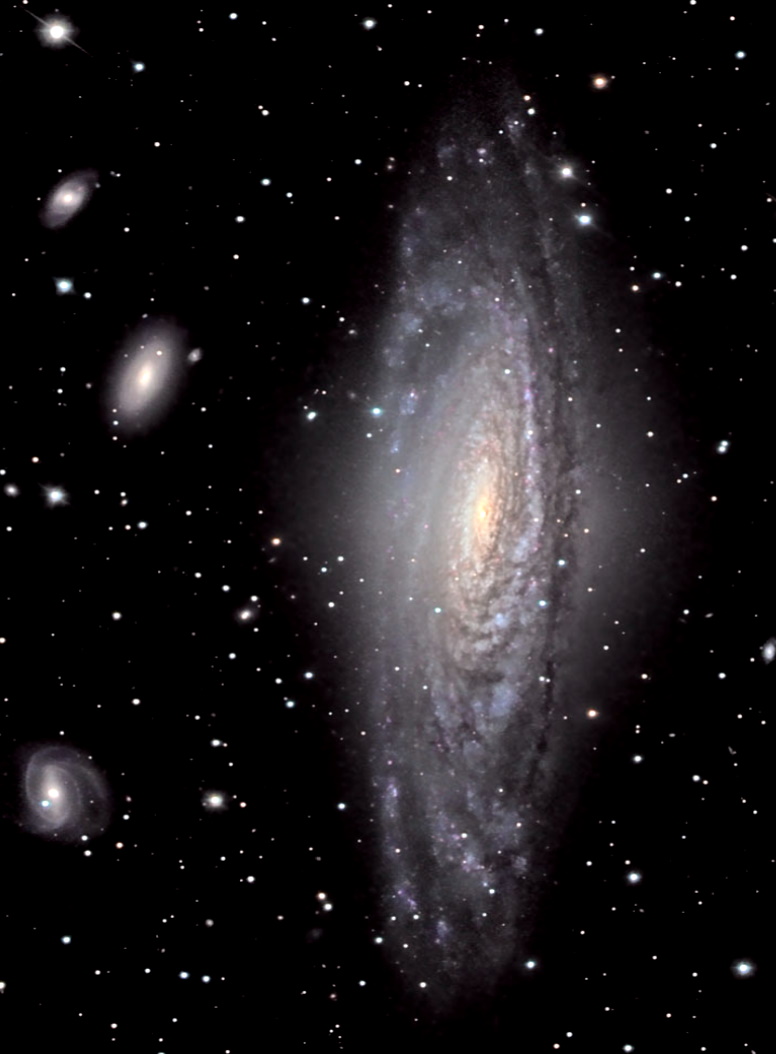
Our Sun and Solar System are whirling around in one arm of our "Milky Way Galaxy". The spiral arms contain dust, gas clouds, and stars, that appear as a "milky" haze that stretches across the evening sky. Most stars in the spherical center, or bulge, of a spiral galaxy are older stars, while younger stars inhabit the outer areas of a spiral galaxy.

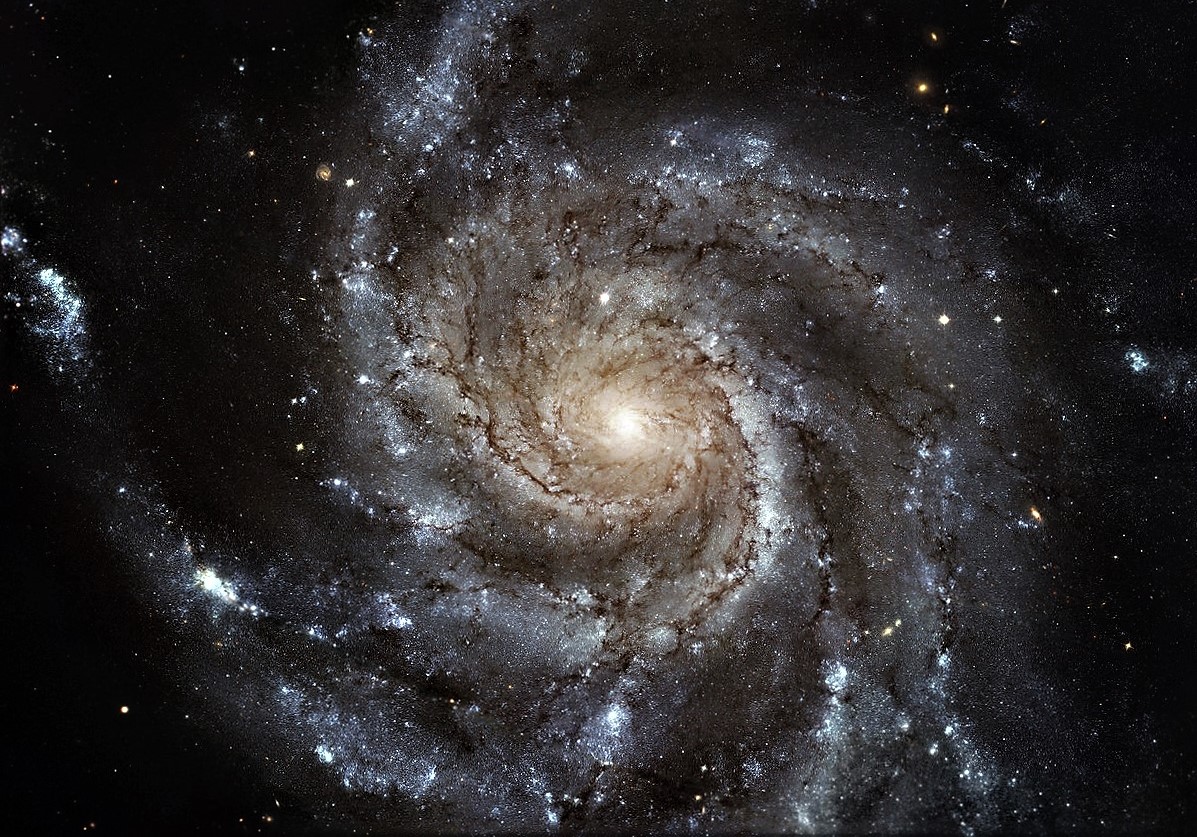
The spacing of the spirals in a spiral galaxy follows an intriguing phenomenon throughout Nature, the
The spacing of planetary distances from the Sun closely correlates with the same ratio of as the ratio represented in each pair of Fibonacci numbers.
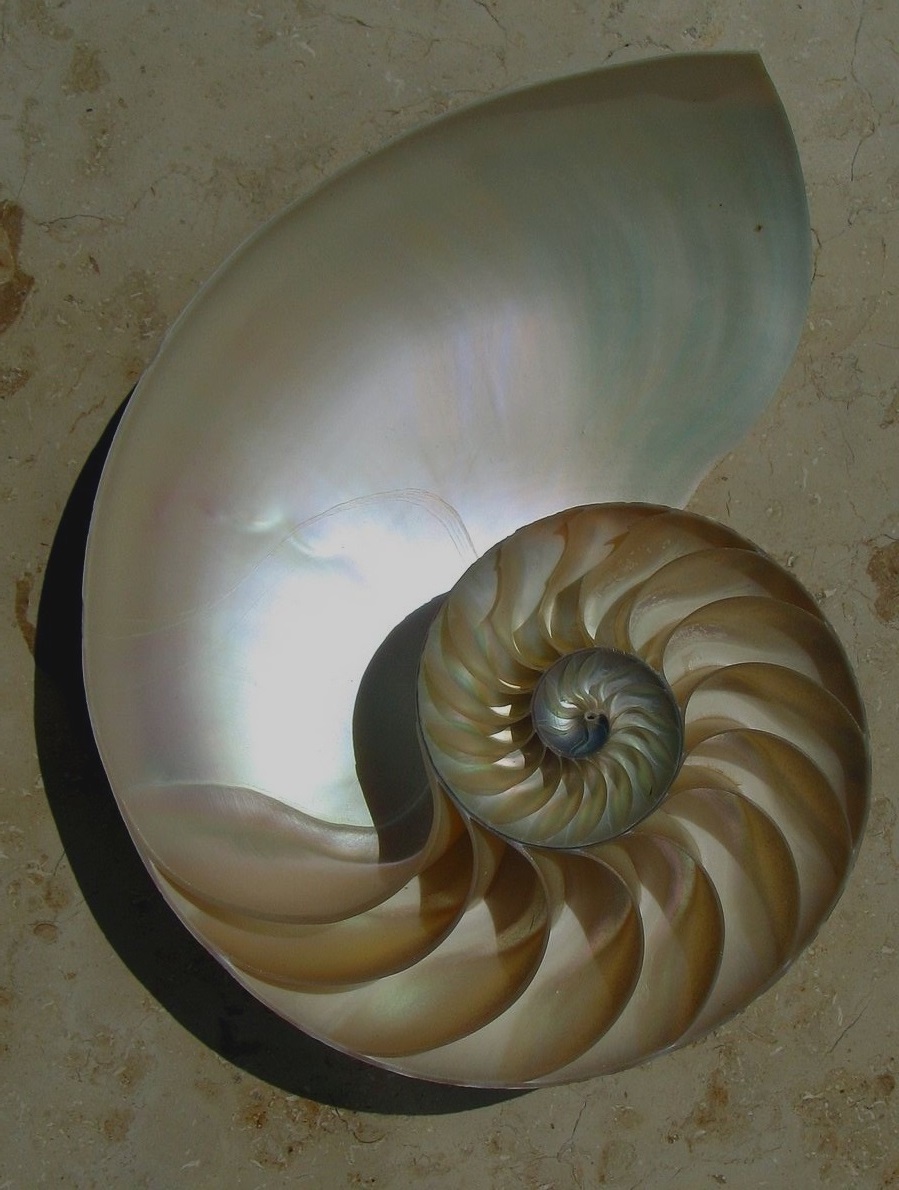
The ratio between each pair of Fibonacci numbers are not only observed in the cosmos, but also observed in geology, biology, and zoology here on Earth. For example, spirally shaped snail shells, hurricane swirls, and the layout of seeds in a plant pod are all arranged according to the Fibonacci Series. This phenomenon is also referred to as the
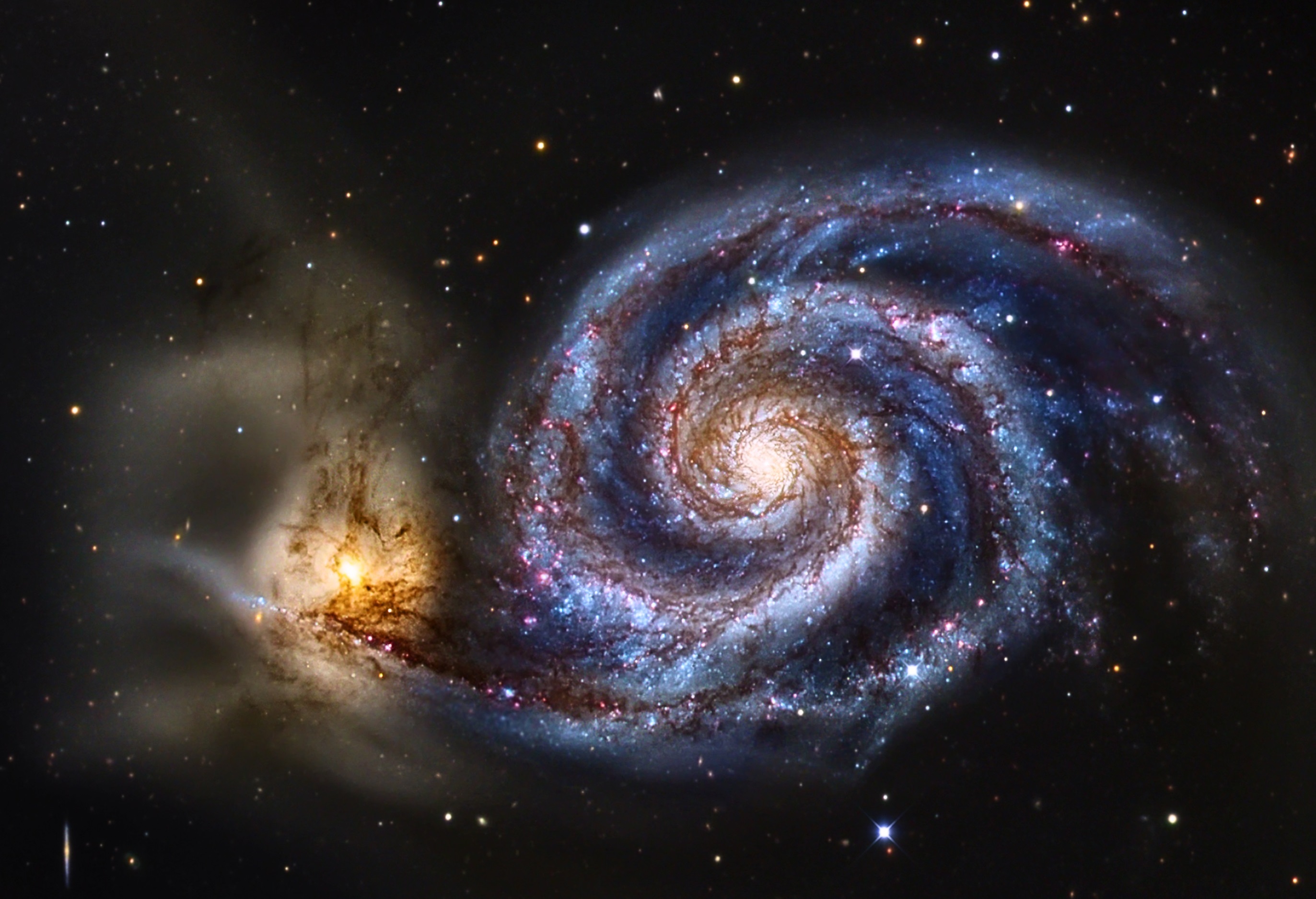

The Whirlpool Galaxy is in reality two galaxies interacting with each other. The streaks of red in the image indicate hydrogen, which indicates regions where stars are born.

Elliptical Galaxies are usually shaped like an ellipse. In visible light, they appear smooth, revealing no features, such as individual stars or dust-laden gaseous clouds. Structural detail, however, is uncovered when these galaxies are viewed in
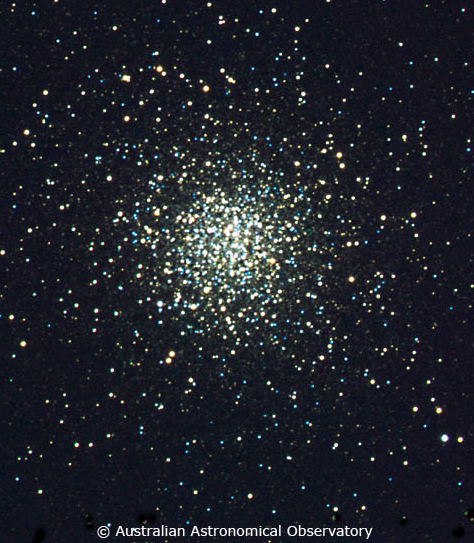

Globular Clusters are spherically shaped

Oddly shaped galaxies that do not resemble any of the more common forms are listed as "irregular" galaxies. Many of these irregular galaxies are among the oldest galaxies in our Universe.

Among the billions upon billions of galaxies and clusters of stars flying around the Universe, the largest and brightest, thus far found, is the dying elliptical galaxy IC-1101 in the constellation Virgo. Containing
Another limiting factor for astronomers was Earth's atmosphere. When viewing the heavans from the Earth's surface, stars appear to be twinkling, though, stars do not twinkle. (Some stars, hovever, do emit pulses of light.) The launching of satellites in the 1960s opened the way to observe the heavens from high above the Earth's surface, for example, the Earth Orbiting Hubble telescope.
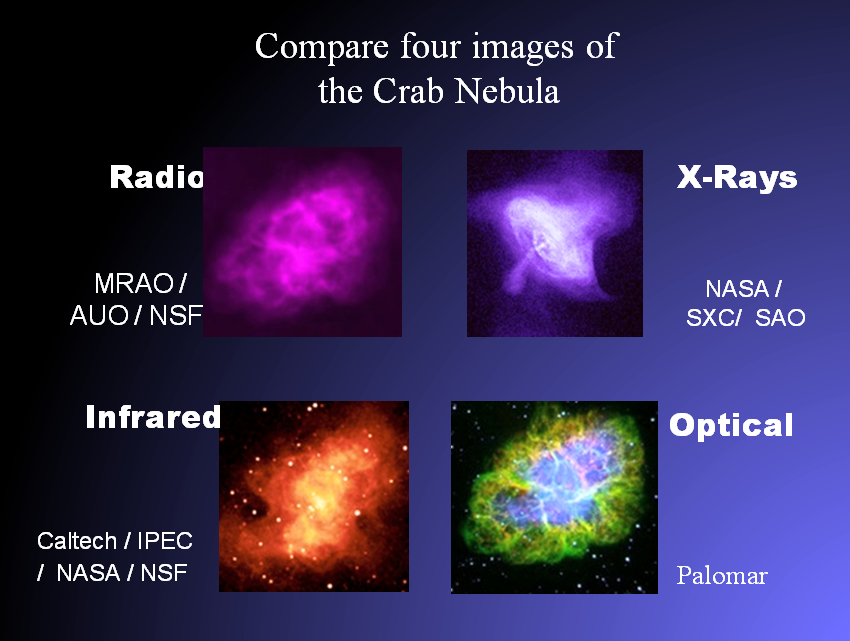
A profoundly limiting factor at the time was the inability to observe objects beyond the limits of human-visible light. Advances in the quality and power of modern telescopes facilitated the way to observe objects in wavelengths beyond visible light. Observing objects in infrared, ultraviolet, and x-ray wavelengths revealed much much more information about individual stars, as well as previously unseen structures within galaxies.
Modern telescopes have drastically increased our ability to see very fine structural detail and to see in many different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, which includes visible light that our human eyes can see. We could say that our Milky Way Galaxy, as well as the Universe itself, has revealed much information about how celestial objects shine for billions of years, how they are born, mature, and die. In the last several decades, we have seen much that was formerly invisible.
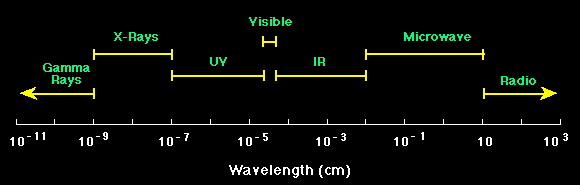
Note: Because "visible light" is a form of "electro-magnetic radiation", the two words are often used interchangeably. Human vision is only a narrow sliver of the total electro-magnetic spectrum.
An aside: many species of insects, birds, and reptiles "see" in parts of the light spectrum that are invisible to humans. A few examples: rattle snakes see in the infrared; many insects and birds see in ultraviolet; dogs see in yellow and blue-to-ultraviolet; and raccoons and dolphins see in black-and-white.

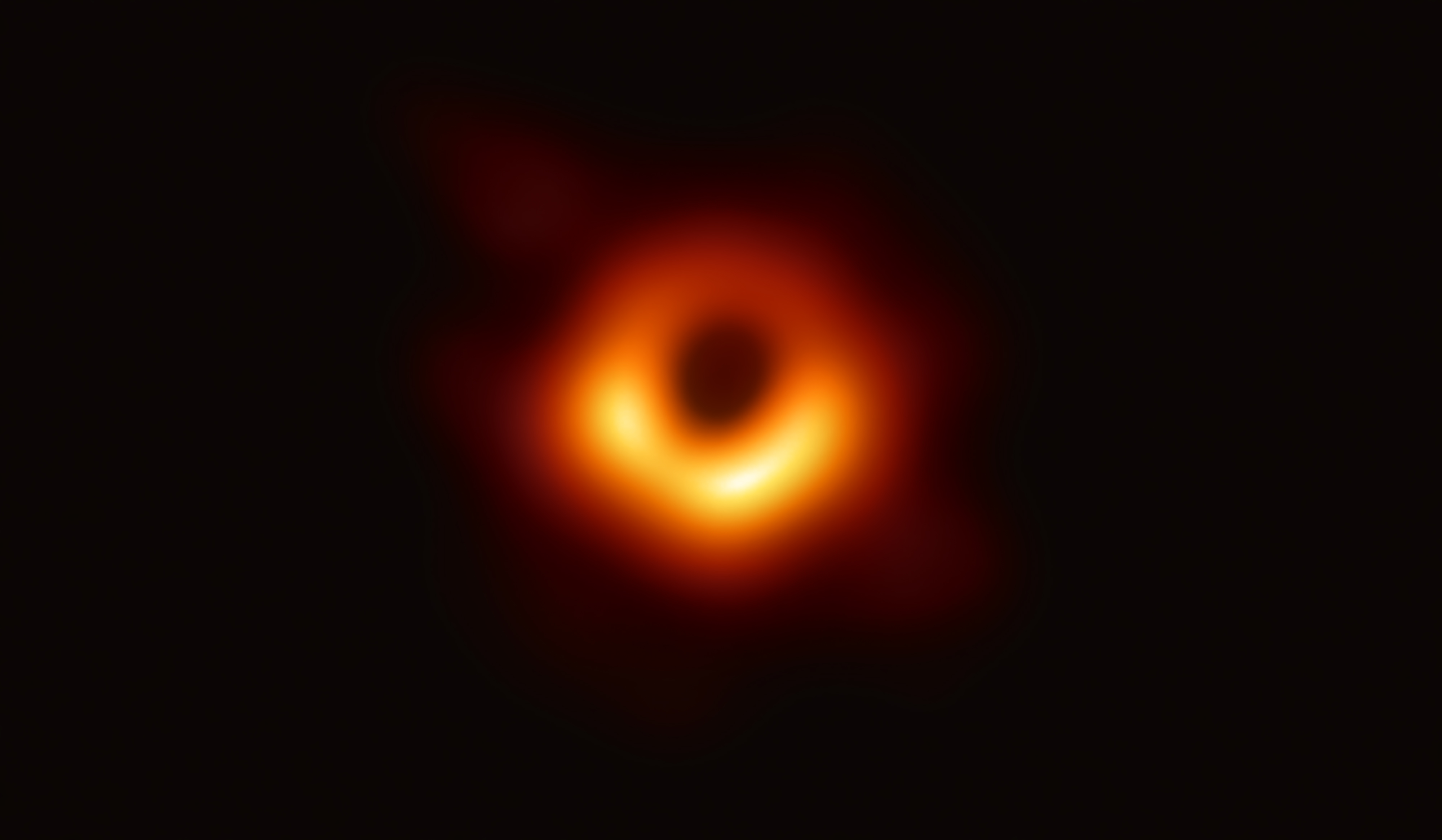
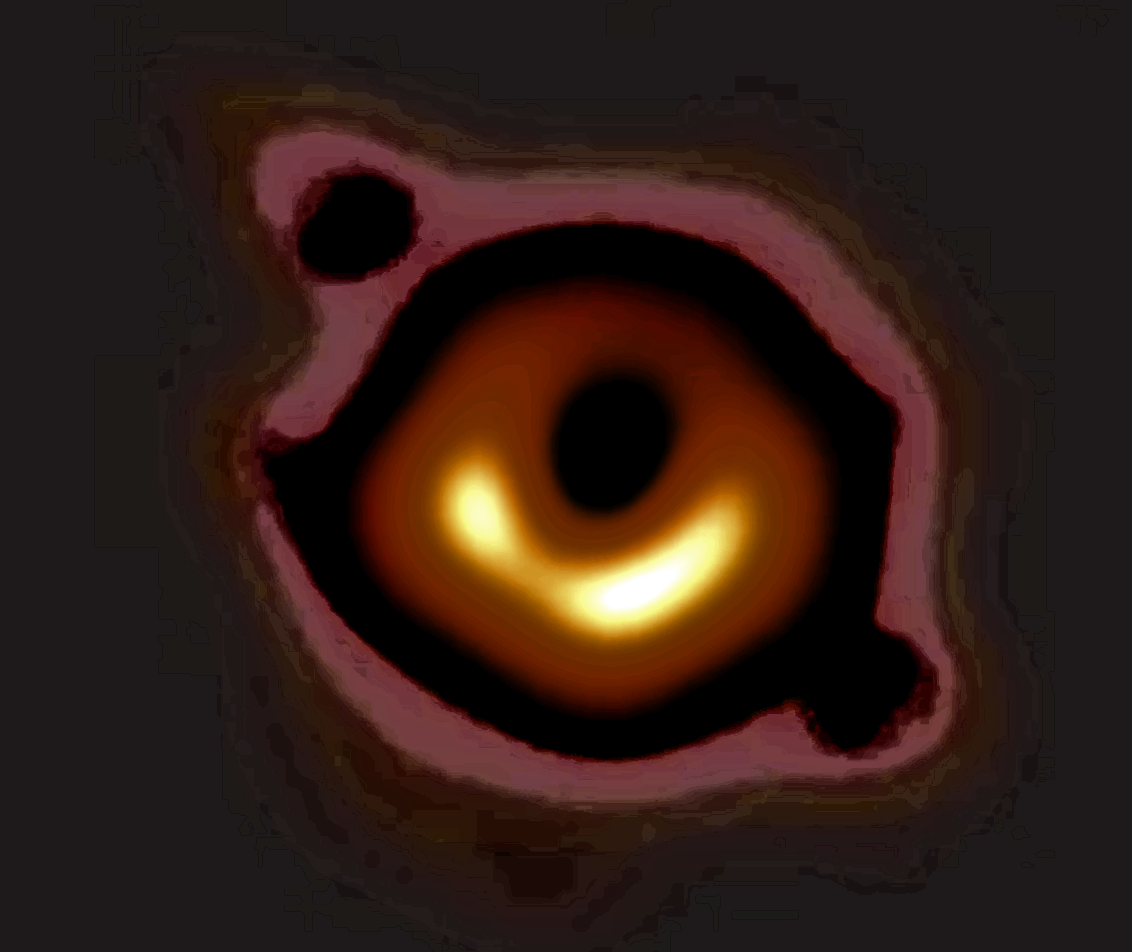
A global group of eight collaborating astronomic institutes in 2019 focused their astronomical multi-meter-wide dish antennas on the massive galaxy M87. From the radio images, dozens of scientists from around the world constructed the first-ever image of a black hole. Although theory had predicted the existence of black holes, no black hole had ever been imaged.
Note: In the modern vernacular, "imaged " replaces "photographed ." Silver-hailide photography has been replaced by solid-state sensors, thus, "imaged".
Also note that the black-hole images are invisible to humans; black holes become visible when viewed at millimeter wavelengths, which is equal to a frequency of .
Black holes are a strange and fascinating phenomenon that have been described as the "vacuum cleaners" of the cosmos. The prevailing theory is that black holes suck up anything that approaches an obserbable ring at the edge of an invisible bottomless pit; this precipice of doom is called by astro-physicists an
The grandest question at the present time is "what is on the

 A multi-inflexion-point gamma filter to the smooth rendition of the original. This author uses the technique to restore the vitality of old photographs.
A multi-inflexion-point gamma filter to the smooth rendition of the original. This author uses the technique to restore the vitality of old photographs.
The black hole image shown here focuses on the center of massive galaxy M-87 by a colaboration of
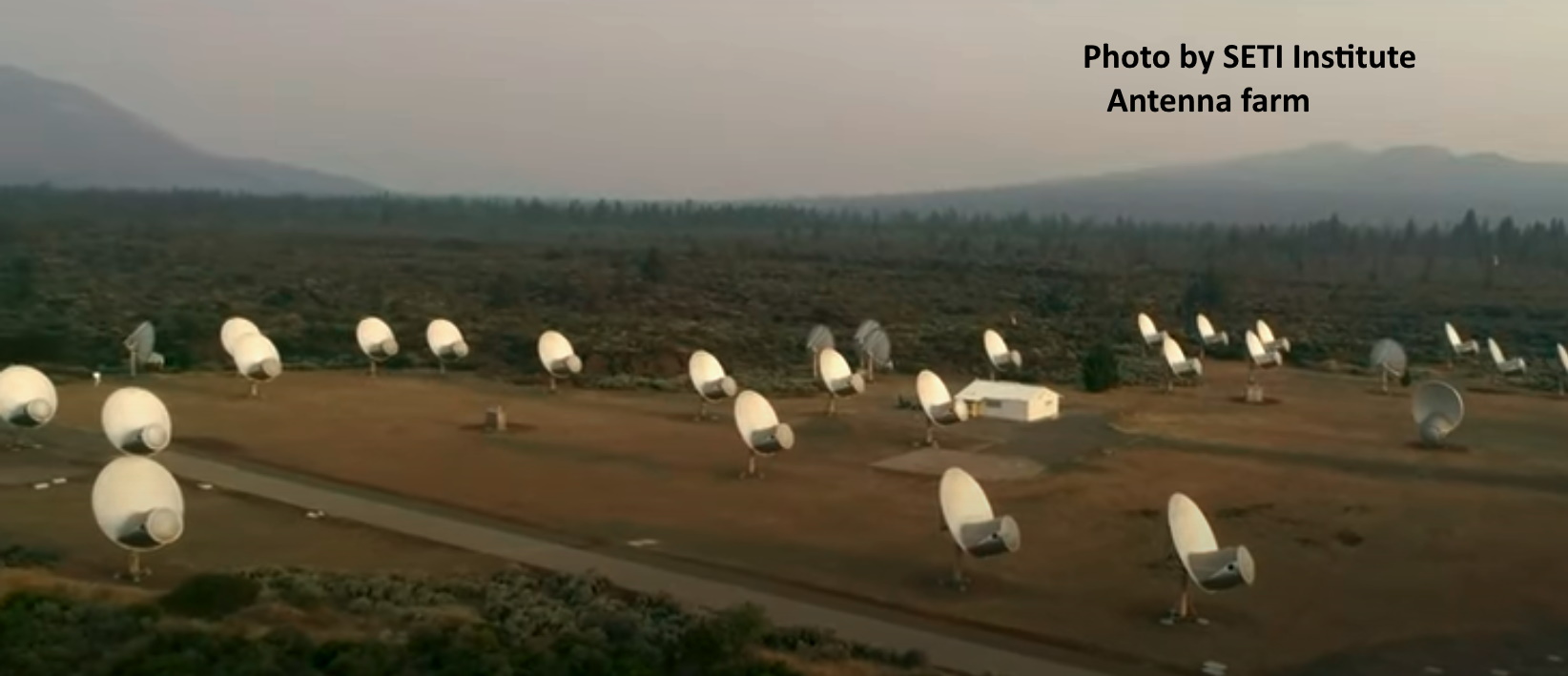
Routine chores for these individual arrays is tracking thousands of orbiting commmunications satellites and monitoring spacecraft journeying through our solar system and beyond. Many of these organizations participate in the search for life beyond Earth.